
UVK Help - Alternate streams manager


You can access this module by clicking Alternate streams manger, in the Home page.
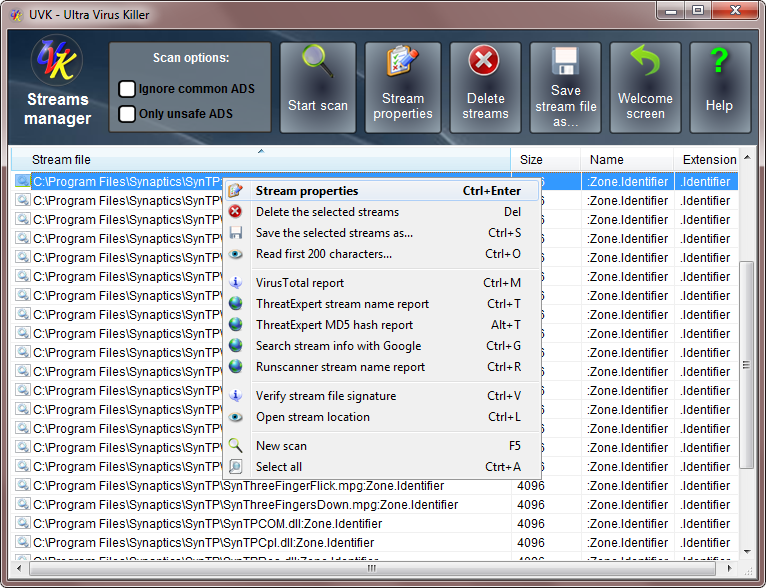
This module lets you search and manage alternate data streams (ADS).
The extract from symantec.com below explains what ADS are.
"Alternate data streams have been around since the introduction of NTFS in the Windows NT operating system. What are alternate data streams though? In essence they were created to provide compatibility with HFS, or the old Macintosh Hierarchical File System. The way that the Macintosh's file system works is that they will use both data and resource forks to store their contents. The data fork is for the contents of the document while the resource fork is to identify file type and other pertinent details.
To this day the existence of alternate data streams is not widely known. However they have been in use by some nefarious individuals in the security community for some time. Whenever something of value is found to further the agenda of malicious hackers and others with ill intent, you can rest assured it will be quickly adopted. There has been a marked increase in the use of these streams by malicious hackers wanting to store their files once they have compromised a computer. Not only that, it has also been seen that viruses and other types of malware are being placed there as well. The crux of the matter is that these streams will not be revealed using normal viewing methods, whether via a command prompt or using the Windows Explorer.
How are these statements corroborated? After an incident has occurred and a computer has been compromised, forensic investigators may be involved. It is based on these findings that the upsurge in the use of alternate data streams has been noted. Even though a corporate entity is well protected, not all anti-virus products in their default configuration will pick up alternate data streams. Most anti-virus products now do find these streams, but only with changes made to the default configuration."
So, these resource forks can be added to any file or directory in a NTFS system by appending ":" followed by the stream name to the file or directory's name. Valid examples are:
C:\Windows:StreamName.exe
C:\Windows\System32\svchost.exe:StreamName.ini
Windows uses this feature to store information about some files. For instance, files downloaded from the internet are added a stream named :Zone.Identifier. This stream is in fact an INI file which has the ID of the zone from which the file was transfered.
This stream is what makes the Windows shell display the dialog "Are you sure you want to open this file? Source:Downloaded from the internet". If you delete this stream, the dialog won't be shown again.
The stream files are not displayed by the windows explorer, which is why you need a dedicated tool like the UVK's stream manager to display them, and delete the eventually dangerous ones. Deleting a stream doesn't delete the file or folder it's associated with.
ADS don't change the size of the file or folder they are forked to, which makes it even more dificult to detect using native tools
Starting a scan for streams:
![]() Select the filter you want UVK to use when scanning by
checking/un-checking the options below Start scan.
Using the Ignore common streams filter will make
UVK ignore common streams created by Windows, such as the
:Zone.Identifier stream explained above. This is the default
procedure.
Select the filter you want UVK to use when scanning by
checking/un-checking the options below Start scan.
Using the Ignore common streams filter will make
UVK ignore common streams created by Windows, such as the
:Zone.Identifier stream explained above. This is the default
procedure.
![]() Using
the Show only unsafe streams will make UVK only
display stream files that can be dangerous for your computer, such
as executable files, DLLs, VB scripts, command line bach scripts,
etc.
Using
the Show only unsafe streams will make UVK only
display stream files that can be dangerous for your computer, such
as executable files, DLLs, VB scripts, command line bach scripts,
etc.
If you un-check both options, all the streams found will be displayed.
![]() Click Start scan to to initiate the scan for ADS.
In the Browse for folder dialog, browse and select
the drive or folder you want to scan. You can stop the scan anytime
by clicking the Stop button in the progress dialog.
Click Start scan to to initiate the scan for ADS.
In the Browse for folder dialog, browse and select
the drive or folder you want to scan. You can stop the scan anytime
by clicking the Stop button in the progress dialog.
Analyzing the streams:
![]() Once the scan is
complete (or interrupted) you can get mor information on the
streams. Select a stream by clicking the corresponding line (hold
Ctrl down to select several lines).
Once the scan is
complete (or interrupted) you can get mor information on the
streams. Select a stream by clicking the corresponding line (hold
Ctrl down to select several lines).
![]() Click Stream
properties in the upper pane or in the context menu to get more info on the stream. UVK will display an
information dialog box similar to the picture below.
Click Stream
properties in the upper pane or in the context menu to get more info on the stream. UVK will display an
information dialog box similar to the picture below.

![]() Clicking the Go button will take you to the
location of the stream file. Note that the stream will not be
visible to the Windows explorer.
Clicking the Go button will take you to the
location of the stream file. Note that the stream will not be
visible to the Windows explorer.
![]() Click
Submit MD5 to VirusTotal to get the VT report of
the stream.
Click
Submit MD5 to VirusTotal to get the VT report of
the stream.
![]() Click
Open Log analyzer to display the contents of the
file in the UVK's log analyzer. Please don't use this feature for
files bigger than 5 MB. Use the Read first 200 characters
context menu instead.
Click
Open Log analyzer to display the contents of the
file in the UVK's log analyzer. Please don't use this feature for
files bigger than 5 MB. Use the Read first 200 characters
context menu instead.
![]() Click
Close (Esc) or press the Esc key
to close the dialog box.
Click
Close (Esc) or press the Esc key
to close the dialog box.
Deleting or exporting the streams:
![]() To delete the selected streams, click Delete streams
in the upper pane or in the right click context menu, and confirm.
To delete the selected streams, click Delete streams
in the upper pane or in the right click context menu, and confirm.
![]() To export the selected streams to common files, click Save
stream as..., in the upper pane or in the context menu,
choose the path where you want to save the stream file, it's name
and click Save.
To export the selected streams to common files, click Save
stream as..., in the upper pane or in the context menu,
choose the path where you want to save the stream file, it's name
and click Save.
Other options:
![]() Use the
other options in the context menu to get more information on the
selected streams.
Use the
other options in the context menu to get more information on the
selected streams.
![]() Click
Start scan or New scan, in the
context menu to start a new scan.
Click
Start scan or New scan, in the
context menu to start a new scan.
![]() Click
Welcome screen or press Esc to go back to the
Home
section.
Click
Welcome screen or press Esc to go back to the
Home
section.
